Best Dental Clinic In Bangalore Indiranagar | Best Dentist in Bangalore Indiranagar
Dental Abscess – Causes, Treatment and Risk factors

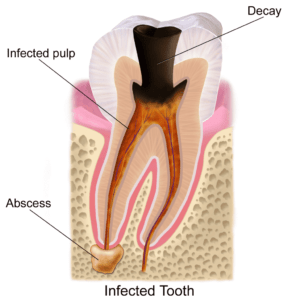
Dental abscess is a pocket of pus that is associated with a particular tooth. It mostly forms around the root of an infected tooth. A dental abscess is also termed as dent alveolar abscess, tooth abscess or root abscess.
There are two common types of dental abscess:
- Periapical abscess – forms at the tip of the tooth’s root.
- Periodontal abscess – affects the bone next to the tooth.
There are other kinds of dental abscesses too like, a gingival abscess that involves only the gum tissue; pericoronal abscess that involves the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a tooth and combined periodontic-endodontic abscess.
Causes of Dental Abscess
A dental abscess is a complication of a dental infection in most cases. Often bacteria that is present in plaque, infects the tooth. Other causes are:
- Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease
- A cracked tooth
- Poor oral hygiene
- Consuming sugary or starchy food/drinks which encourages growth of bacteria
- An injury caused to the tooth
- Previous tooth or gums surgery
- Certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, and those having treatment, including steroid medication, chemotherapy, etc.
Dental Abscess Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a dental abscess include:
- Sharp pain in the affected tooth that may come on suddenly and gradually worsen
- Pain that has spread to the jaw, ear, and neck
- Pain that’s worse when lying down
- Sensitivity to hot or cold food and drinks
- An unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Difficulty in swallowing
Treatments for dental abscess
Dental abscesses are treated by removing the source of the infection and draining away the pus. Successful treatment of a dental abscess centers on the reduction and elimination of the offending organisms. This can include treatment with antibiotics and pus drainage. If the tooth can be restored, root canal therapy can be performed. Non-restorable teeth must be extracted, followed by curettage of all apical soft tissue. Here are a few treatments that are used: (Local anesthetic will usually be used to numb your mouth for these procedures.)
1. Incision: The abscess needs to be cut out and the pus needs to be drained out.
2. Treating periapical abscess: In order to treat a periapical abscess, root canal procedure will be used. A hole will be drilled into the dead tooth and the pus will be drained out. If there is any damaged tissue, that will be removed from the pulp. After this, a root filling is inserted into the hole to prevent subsequent infections.
3. Treating periodontal abscess: Once the abscess is drained and the periodontal pocket is cleaned, the dentist will use the scaling and planning method below the gum line to smoothen the surfaces of the root of the tooth. This will help the tooth prevent further infections. If the infection spreads, antibiotics will be prescribed.
Preventing dental abscesses
Reduce your risk of developing dental abscesses by keeping your teeth and gums as healthy as possible.
To do this, you should:
- Floss and brush at least once a day to clean between your teeth and under the gum line
- Use a good fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth twice a day at least for 2 minutes each time
- Cut down on sugary and starchy food and drinks
- Keep a regular check on your oral health by visiting your dentist regularly
Risk factors associated with Dental Abscess
At times, dental abscess will not heal by following the treatments detailed in the treatments section above, In such a case, it will be treated with surgery and filling the root tips; and will also require a biopsy to evaluate the diagnosis
If left untreated, a severe tooth abscess may become large enough to perforate bone and extend into the soft tissue eventually becoming osteomyelitis and cellulitis respectively. It can then spread internally or externally.
In cases of severe complications, like Ludwig’s angina (which is a combination of growing infection and cellulitis, that closes the airway space and causes suffocation in extreme cases) requires immediate hospitalization.
Also, if the infection spreads down the tissue spaces to the mediastinum, it can have dire consequences on the vital organs such as the heart.
There could be a possibility of another complication, which is mostly from the upper teeth – That is the risk of septicaemia (infection of the blood) from connecting into blood vessels, brain abscess or meningitis.
If you have any of the above mentioned symptoms or if you are suffering from Dental abscess, do not assume it will get better on its own. You need treatment from a specialist who can help save your tooth – dentist or endodontist. If you don’t treat it, the infection can spread to other body parts and cause major complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is a dental abscess?
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection, typically forming around a tooth’s root (periapical abscess) or in the bone next to the tooth (periodontal abscess).
Q. Can a dental abscess heal on its own?
No. Dental abscesses require professional treatment. Without care, the infection can spread and lead to serious complications.
Q. How can I prevent a dental abscess?
- Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Limit intake of sugary and starchy foods
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings
- Address dental issues promptly before they escalate
Q. What are the risks of leaving a dental abscess untreated?
Untreated abscesses can spread, causing bone loss, tissue infections (cellulitis), Ludwig’s angina, septicaemia, brain abscess, meningitis, or damage to vital organs like the heart.