- +917892951808
- Indiranagar, Bangalore
Best Dental Clinic In Bangalore Indiranagar | Best Dentist in Bangalore Indiranagar
- Home
- About Us
- Treatments
- Blog
- Contact Us
Periodontitis – Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options

The word “periodontitis” comes from “periodontium”, which means “surrounding (peri) the tooth (odont)”. Periodontium includes all the components that hold the tooth in the jawbone: the gum (gingiva), the bone, and the Cementum – the anchoring structure on the surface of the root. The periodontium surrounds the entire root.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that causes severe gum infection and damages the soft tissue. Around 40 percent of people suffer from periodontitis. Among adults, it is estimated that around 70% of tooth loss is caused by periodontitis. If periodontitis is left untreated, it can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss. It can also lead to other health problems.
Although Periodontitis is extremely common it can be largely prevented if gum disease is diagnosed at early stages. It's usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily and getting regular dental checkups can greatly improve your chances of successful treatment for periodontitis and can also reduce your chance of developing it.
Periodontitis can then lead to problems with speaking, chewing food, as well as causing aesthetic damage to your smile.
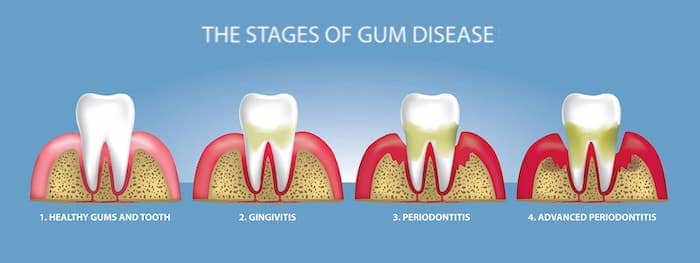
What are the stages of gum diseases?
Have you been noticing blood in the sink every morning after brushing? Or notice blood on that Apple bite? That bleeding can be one of the first warning signs of gum disease. As mentioned at the onset, when the disease is mild, it is called gingivitis and only the gums are infected. If this is left untreated, the infection will travel below the gum line and into the bone, causing a more serious form of gum disease called periodontitis.
Both these oral health issues – gingivitis and periodontitis – not only affect dental health but have also shown to carry other health risks – like diabetes, heart disease, osteoporosis, pneumonia, and cancer.
The progression of gum disease isn't an overnight process. It happens in 2 stages.
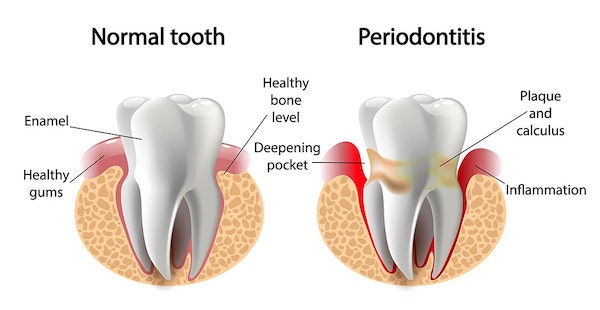
How the Periodontal pocket is formed?
Dental plaque or bacteria grows and accumulates on the tooth and within the mouth. These bacteria use food particles and saliva to grow and multiply. The gums then start bleeding and swelling occurs which is known as gingivitis.
In order to get rid of the bacteria, the body produces chemicals to attack the bacteria which in turn harms or destroys the bone and ligaments holding the teeth in place. This causes loosening of the tooth and thereby forming a pocket. Over a period of time, these pockets get deeper, providing a larger space for bacteria to live. These deep pockets result in major bone and tissue loss, eventually leading to the extraction of the tooth.
A pocket depth varying from 1mm-3mm indicates gingivitis – an early stage of gum disease. Depth of 4mm-5mm indicates mild periodontitis infection, depth of 6mm-7mm indicates moderate periodontitis infection and 8mm and above indicate severe periodontitis infection causing a higher risk of permanent damage.
1. Gingivitis (Gum level infection)
Periodontitis begins with gingivitis – inflammation of the gums. This is the body's response to bacteria that has been accumulated on the teeth. The symptoms usually involve red, swollen gums and bleeding especially while brushing or biting on food. Unlike periodontitis , Gingivitis is an inflammation that is limited to the gum line, there is not yet any loss of the structures that hold teeth in place; while in periodontitis there is loss of the jawbone, periodontal ligament, and root cementum.
2. Periodontitis (Bone level infection)
Gingivitis, if not treated in time, can turn into periodontitis,
- Mild periodontitis: At this level, the gum disease begins to destroy the bone and tissue that support the teeth. The bacteria evolves and is more aggressive, which causes additional bone loss.
- Moderate periodontitis: The process of destruction continues and the gums continue to fall away from the tooth thereby making a huge depth or pocket for the accumulation of bacteria to attack not only the bones but also the immune system.
- Severe periodontitis: This is the final stage where there is extensive bone loss and tissue damage. Also, there is pus formation at this level. In this case, the tooth or teeth are often extracted.
Treating periodontitis and advanced levels of periodontitis requires more than good oral hygiene at home. It needs professional care from a dentist or periodontist.
What are the symptoms associated with Periodontitis?
One of the first signs is bleeding gums. The gums may look red and swollen and you might notice a discoloured layer of bacterial plaque on the teeth. If not removed through proper cleaning of the teeth, this plaque will turn into hard deposits known as calculus or tartar, which cannot be removed by a toothbrush and you need a dentists.
Here are some obvious signs and symptoms of developing periodontitis –
- Bleeding gums caused due to brushing or biting chewy hard food
- Bad breath
- Changes in the positioning of the teeth in the jaws.
- Receding gums – Where teeth appear longer
- Constant unbearable pain
- Teeth sensitivity
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Periodontitis starts with a plaque and tartar buildup. Our mouth is home to 700 different species of bacteria, most of which are harmless. But when we do not clean our teeth well enough, bacterial deposits build up next to the gums, forming a “plaque” – which creates favourable conditions for more dangerous bacteria to flourish. When this happens, natural defences of the body are also compromised too. Plaque forms on your teeth when starches and sugars in food interact with bacteria normally found in your mouth. When plaque hardens under the gumline it turns into tartar which is filled with bacteria and the longer plaque and tartar remains on your teeth, the more damage it can cause.
Additionally, ongoing gum inflammation can cause periodontitis.
Risk Factors associated with Periodontitis or Periodontal Disease –
There are several factors that increase your chance of developing periodontitis. Here are some of the many –
- Smoking
Smokers are much more likely to develop periodontitis than non-smokers.. In smokers, gum bleeding may be less noticeable. This is because of the effect of nicotine on blood vessels, which means that the progress of the disease may be hidden. However, a dentist can detect signs of the disease much earlier, during a routine dental examination. Hence make sure to visit your dentist regularly, especially if you have been in the habit of smoking.
Smokers experience greater bone loss and are more likely to develop gum pockets that house a greater number of harmful bacteria. Quitting smoking is the best option.
- Genetics
The way our immune system reacts to harmful bacteria can differ from person to person because of genetic differences. Hence, genetics plays an important role in how fast gum disease progresses.
- Age
Older people have more severe cases of Periodontitis than younger ones. Although it might start young and you may fail to notice until you reach a certain age.
- Type-2 diabetes
Periodontitis and diabetes have a two-way effect on each other. Those whose blood sugar is not well managed have a higher risk of developing periodontitis. Also, patients suffering from periodontitis have a higher risk of suffering diabetes.
[Read: The Connection Between Diabetes and Gum Disease]
- Poor diet
An unhealthy diet especially high in processed foods and refined carbohydrates increases the tendency for gums to become inflamed. An unhealthy diet filled with sugar can also increase the risk of diabetes, which can further worsen periodontitis.
- Stress
Mental and emotional stress can weaken the immune system and lower the resistance of the gums to harmful bacteria. People with a weakened immune system may be more susceptible to gum disease.
Are children at Risk of Periodontal Disease?
Children are more likely to have gingivitis, the mildest form of the disease. Children who don't brush their teeth after snacking and consuming fizzy drinks may develop gum disease. Sugar, starchy food like fries feed the acids that erode the tooth enamel.
An increase in hormonal levels during puberty can also make some teenagers more susceptible to gum disease. Some girls may notice bleeding gums before their menstrual cycle begins.
How to Prevent Periodontitis or Periodontal Disease?
Gum diseases can be prevented at early stages by regularly maintaining your oral hygiene – By brushing and flossing regularly. Also, regular dental visits
Here are a few tips to maintain good oral hygiene:
- Clean between teeth using interdental brushes and dental floss.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, for at least two minutes.
- After brushing your teeth, antiseptic mouthwashes can be used to prevent plaque accumulation for up to 12 hours.
- Special care should be taken when there are additional fillers in the mouth like implants or crowns. Thoroughly clean around crooked or crowded teeth, and around fillings, because plaque builds up easily in such places as they are hard to access.
Lastly, it is important to consult your dentist or dental hygienist on the techniques to use at home to keep gum healthy.
Consequences of Periodontal Disease –
- Discomfort while eating – Since periodontitis weakens the structures that hold the teeth in place, teeth become loose and it causes problems while chewing the food. This can also affect digestion. If the damage continues – and especially if teeth are lost – you will only need to consume soft food.
- Tooth loss: In severe cases of periodontal inflammation, the supporting structures of the teeth – including the surrounding bone – are destroyed. This will eventually cause the teeth to loosen – and you will either lose it or it will have to be extracted.
- Speech Difficulties – Loose teeth caused by periodontitis can make it difficult to speak words clearly. If the visible front teeth in the upper jaw are forced apart because of periodontitis, the gaps that arise can cause problems in speaking.
- Appearance Distorted – People with periodontitis can have aesthetic problems. Gums are dark red because of inflammation, teeth look longer because of receding gums, and the roots become visible – all of which can cause aesthetic problems. As teeth loosen, they can move apart leaving dark spaces between them, and if teeth are lost as a result there can be unattractive gaps.
- Bad breath: The bacteria that causes the inflammation also causes bad breath. The kinds of bacteria that cause periodontitis grow in gum pockets and produce foul-smelling sulphur compounds. Maintaining good oral hygiene is one way to keep bad breath away.
- Negative effects on general health: Gum disease or periodontal disease is associated with a lot of systemic diseases and health problems. The effects of periodontitis are directly associated with the extent of the infection and untreated duration of the gum disease. Periodontitis means an increased risk of heart disease, suffering from diabetes, cerebrovascular disease, and complications in pregnancy (premature birth and low birth weight due to periodontitis).
In fact, did you know – periodontitis has been linked to more than 50 diseases and conditions, including Alzheimer's Disease, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and certain types of cancer.
Also, about 70% of the tooth loss is because of advanced levels of Periodontal disease.
Diagnosis of Periodontitis or Periodontal diseases
There are several stages involved in diagnosing periodontitis.
- Clinical examination
A clinical examination is the only way to assess the condition of the gums and the tooth-supporting structures.
An initial check-up will quickly determine whether you are suffering from gingivitis or periodontal disease. The dentist will use a periodontal probe and the depth of penetration at the gum line will be measured gently and precisely at various sites in the mouth. The probe measures the distance between the gum line and the end of the pocket. At healthy sites, the probing depth is 3mm or less, but where periodontitis is present, the depth is 4mm or more.
If the dentists suspects and diagnoses periodontitis, further tests will be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and start the treatment. A periodontal chart is used to precisely record the height of the jawbone.
- X-rays
After the clinical examination, an X-ray needs to be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Only two images – “bite-wing” images are needed, but more extensive cases may require a panoramic X-ray of the whole mouth or up to 14 additional X-rays. These X-ray images show the jawbone surrounding the tooth and make it possible to estimate and understand the severity of bone loss.
- Microbiological tests
Microbiological tests examine specific harmful bacteria composition. The results of these tests can provide information that will enable the periodontist to provide appropriate care, treatment and avoid unnecessary surgery, if not required.
- Classifying the disease
Cases of gingivitis and periodontitis can be classified using a classifying system. Cases of periodontitis are classified according to four stages and three grades. The stages describe the severity and extent of the disease, while the grades describe the likely rate of progression. By classifying cases of periodontitis in this way, dentists and periodontists can provide the appropriate form of treatment for each patient based on the severity.
Treatment For Periodontitis or Periodontal Disease
Treatments are categorised into Surgical and Non-surgical. Typical non-surgical treatment for periodontal disease is scaling and root planing (SRP).
Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from tooth surfaces and from underneath the gums. It may be performed using instruments, a laser or an ultrasonic device. Root planing levels the root surfaces, and stops the further buildup of tartar and bacteria and kills bacterial byproducts that are known to contribute to inflammation and slow healing.
In the surgical method, there is the option of traditional practice of Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery). In this the periodontist makes small incisions in the gum so that a section of gum tissue can be elevated back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Since periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be recontoured before the gum tissue is put back in place after suturing. This method can be more painful and hence people look for alternatives. One of the alternatives is the wavelength optimised Periodontal Therapy.
- Wavelength optimized periodontal therapy or WPT is a minimally invasive method to treat periodontal diseases using Nd: YAG and ER: YAG laser energy. These two wavelengths have unique clinical and therapeutic abilities and are used to treat periodontal diseases in the best way. Instead of a sharp knife that would peel off the gum or teeth, thin laser quartz would be inserted between the tooth and the gum line to remove the diseased tissue.
Wavelength optimised Periodontal Therapy is carried out in 4 simple steps:
- The Nd: YAG laser destroys the diseased epithelial lining of the periodontal pocket and improves access to the root surface.
- The Er: YAG is used to remove microbial biofilm and calculus from the root surface.
- The Nd: YAG laser energy is used to harden and helps to form a stable fibrin clot. This seals off the pocket and promotes healing and bone regeneration.
- Lastly, endotoxins from the root surface and epithelial lining are removed.
At Dental Solutions, Bangalore, we have successfully treated patients having severe periodontitis with Wavelength optimised periodontal therapy.
We are proud to be among the few best dental clinics in Bangalore that offer laser dentistry along with other latest dental technologies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-1LWXwNHCRc
- Oral-hygiene Maintenance
The oral-hygiene phase of treatment is to reduce bacteria growth in the mouth and thereby reduce the level of inflammation. The dentists will explain the causes of your periodontitis and underlying concerns if any. They will provide clear instructions on how to keep your teeth and gums clean. You will be given advice on how to use different tools and techniques: for example, the various tooth-brushing techniques and the correct use of dental floss, and antiseptic mouthwashes.
- Professional cleaning
You need to visit the dental clinic to conduct a professional cleaning. In this setting, all bacterial deposits are removed from accessible areas of the teeth, and the teeth are treated with fluoride and polished. If required, the dentist will also remove all bacterial deposits and tartar from the gum pockets or root surfaces.
- Antibiotic therapy
If oral hygiene methods do not work in controlling the mild gum disease phase, antibiotics are administered.
- Reassessment
Weeks after diagnosing gum disease, your dentist or periodontist will make a full assessment of your gums. They will use the periodontal probe to record the depth of any periodontal pockets, check for inflammation and bleeding of the gums. If periodontal pockets greater than 3mm are still present, further treatment options will be suggested as required, including corrective surgical therapy.
At Dental Solutions Bangalore, we use advanced technology to treat periodontal disease. If you have been suffering from gum disease for a long time, and not sure how to find the right solution – drop by at our – We have all the dental solutions for your oral health concerns
