Gum Recession – Causes Symptoms Treatment and Prevention
Gum Recession – Causes Symptoms Treatment and Prevention
Gum recession is a condition where your gums pull away from your teeth. It is caused by many things, including aggressive brushing, smoking, and even genetics. Treatments are antibiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses and surgery. Once you have gum recession, it cannot be reversed. However, dental treatment can prevent the prognosis from worsening.
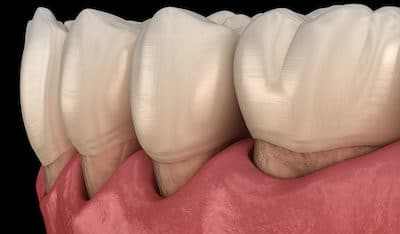
What is gum recession?
Gum recession is a gum disease that happens when your gum tissue is pulled away from the teeth, leaving your teeth exposed. Gum recession makes your teeth more vulnerable to cavities and can cause an ache while brushing or eating. Gum recession can be mild, moderate, or severe, affecting one tooth or several teeth.
Who does gum recession affect?
Gum recession is a common condition, especially for people over 65. You are more likely to develop gum recession if you:
- Have periodontal disease
- Have a tongue or lip piercing.
- Had orthodontic treatment or braces
- Chew tobacco.
- Brush teeth aggressively.
How common is gum recession?
Gum recession is a common dental problem. Approximately 88% of people over the age of 65 have gum recession on one or more teeth.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of gum recession?
The most common sign of gum recession is exposure of the tooth root. Other warning signs of gum recession include:
- discomfort or pain near your gum line.
- Sensitivity to heat, sweets, and cold.
- Sensitivity when flossing and brushing your teeth.
- Sensitivity during dental cleanings.
Gum recession can lead to other oral health issues, such as tooth mobility or losing teeth. If you're experiencing any of the signs listed above, contact your dentist immediately.
What causes recession of gums?
Your gums may recede for various reasons. Few Gum recession causes include:
- Brushing too hard and or aggressively.
- Dental plaque or tartar build-up.
- Periodontal disease.
- Trauma or injury to the gum tissue.
- Wrong tooth positioning (misalignment).
- Smoking or chewing tobacco use.
- Lip and/or tongue piercings.
Periodontal diseases: Gum disease (also known as gingivitis) is a bacterial infection of the gum tissue. It can progress and destroy the supporting bone around your teeth. Gum tissue gives your teeth their firm anchoring in place. Your genes may determine if you are more susceptible to getting gum disease. Studies show that 30% of the population is likely to experience gum recession regardless of how well they care for their teeth.
Aggressive tooth brushing can cause the enamel on your teeth to wear away and your gums to recede.
- Insufficient dental care: As a result of an inadequate cleaning routine, plaque will turn into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dentist. Tartar leads to gum recession. Plaque is a hard substance that builds between your teeth and can only be removed by professional dental cleaning. Plaque can lead to gum recession.
- Hormonal changes. The hormone level in a woman's body can change throughout her lifetime, and fluctuate during periods of puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. These shifts can be responsible for gum recession.
- Tobacco products. For those who chew, smoke, or dip tobacco, plaque can be difficult to remove and responds differently to toothbrushes.
- Repeatedly clenching or grinding your teeth can be harmful, as it places a lot of stress on the teeth. This can result in receding gums.
- A crooked smile or misaligned bite can cause gum recession and may eventually lead to tooth loss.
- Body piercing of the tongue or lip. Jewelry can rub the gums and irritate them to the point that gum tissue is worn away.
The causes of gum recession could be varied, but the most likely cause is poor oral hygiene. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the long-term problems that a problem like gum recession could cause.
How is gum recession diagnosed?
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession. They check how much gum has receded on your teeth with a special instrument called a periodontal probe.
If your dentist sees gingivitis or periodontal disease, they will check to see how deep your pockets are. Healthy pockets should measure around 1-3 millimeters while gingivitis is around 4 millimeters. If you have periodontal bone loss, areas of gum recession will be more than 5 millimeters deep around each tooth.
Management and Treatment
Can gums grow back?
Gum recession is an ongoing process, and if you do not take proactive steps to prevent it, it will worsen.
How can I reduce sensitivity caused by gum recession?
Have you noticed your gums receding? Because your roots are covered with cementum, which is not as strong as enamel. You can use fluoride varnish or a desensitizing toothpaste to reduce the pain you experience because of gum recession or have a numbing mouth rinse to make yourself more comfortable during dental cleanings.
What's the best toothpaste for gum recession?
Combined with the other treatments discussed above, desensitizing toothpaste can help to relieve discomfort associated with gum recession. You can find ingredients such as potassium nitrate, stannous fluoride, arginine, and strontium chloride in many desensitizing toothpastes. Long-term use of these will have a higher success rate over short-term use.
How do they fix receding gums?
How you treat gum recession depends on what caused the condition. If it's due to a milder condition, you may improve symptoms with antibiotics or orthodontics. Surgery, however, is typically needed to address severe cases of gum recession.
Nonsurgical treatments
Nonsurgical treatments for gum recession may include:
- Topical antibiotics. If you suffer from gum recession, the treatment will depend on what caused the condition. Mild cases may be improved with nonsurgical treatments like antibiotics, bonding, or braces. In most cases though, surgery is needed to fully correct it.
- Dental bonding. Sometimes, your dentist can camouflage the area of recession with tooth-colored composite resin. This covers your exposed tooth root and makes it more comfortable.
- Orthodontics. The other option for teeth that are crooked, tipped or rotated is dentistry. Once the tooth is aligned, many times the gum would self adjust and heal on its own over time.
Gum recession surgery
Gum graft surgery Gum graft surgery is the best way to treat gum recession. A periodontist, a specialist in gums, applies this procedure. They replace missing gum tissue with a gum graft during surgery.
Your gum graft can come from tissue taken from the roof of your mouth or from the scalp. Once your doctor fixes the graft in place, they attach it with stitches. They do this minimally-invasive procedure to repair an injury.
Open flap scaling and root planing: The procedure for gum disease is a scaling and root planing. By folding back the tissue and removing harmful bacteria, the doctor can restore healthy looking gums.
Regeneration: If the bone supporting the teeth has been damaged as a result of gum recession, a procedure to regenerate the lost bone and tissue may be recommended. As in pocket depth reduction, the dentist will fold back the gum tissue to remove the bacteria. A regenerative material, like a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-stimulating protein, will then be applied to promote the body to naturally regenerate the bone and tissue in that area. After the regenerative material is put in place, the gum tissue is secured over the root of the tooth or teeth.
Soft tissue graft: Soft tissue grafts are procedures where gum is surgically removed and then stitched onto the surrounding gum. The types of gums you can get surgically replaced depend on your specific problem and situation. The most common type of soft tissue graft is called a connective tissue graft, where the skin is cut at the roof of your mouth (palate) and then the flap removed, before stitching the flap back down.
Dental grafts can come from your palate or from the roof of your mouth. If you have enough tissue to keep the tooth, then a pedicle graft is a good option.
Your dentist will determine the best type of procedure that you need to make you feel better depending on the individual case.
How long does it take to recover from gum grafting surgery?
You should feel back to normal in only two weeks following gum recession surgery. Several factors will determine how long it takes you to recover, including if your graft came from the gum or if a traditional procedure was used.
After surgery, follow the instructions of your surgeon closely to foster a comfortable recovery.
Prevention
Can I prevent gum recession?
Preventing Gum recession can be difficult, particularly if you are genetically predisposed to thin gum tissue. but if you practice proper teeth and gum care you can significantly reduce your risk of infection-related gum recession. For example
- thoroughly Brush your teeth twice every day.
- Floss everyday
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash twice daily.
- Follow your dentist's suggestions for teeth cleanings. (Many can maintain healthy gums with 6-month cleanings, but some may need more frequent visits.)
- Use soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Don't smoke or chew tobacco.
See your dentist if you notice any signs of gum recession.
Outlook / Prognosis
What can I expect if I have gum recession?
If your dentist believes you are experiencing gum recession, they will often prescribe some non-surgical treatments, such as topical antibiotics or dental bonding. If the problem is more severe, you will usually be referred to a periodontist or oral surgeon for a consultation about gum grafting.
Is gum recession curable?
Gum recession can't be cured, but with proper care and treatment, it can be managed.
Living with
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you notice that your teeth' roots are more visible or that your teeth have increased sensitivity, then you have gum recession. It is important to call your dentist at the first sign of a problem. The sooner gum recession is detected and treated, the better chance you have of establishing good oral health.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
Learn what kinds of problems gum recession might cause, and what questions to ask your dentist about gum recession.:
- How advanced is the gum recession?
- Are there any non-surgical options that could work?
- If not, what type of surgery do you recommend?
- What are the chances of gum recession coming back?
- How often should I get my teeth cleaned?
A note from Dental Solutions Clinic
Gum recession is a severe oral health problem that includes a lack of gum coverage and has the potential to cause major problems. Pain and sensitivity are some of the signs, though you should get an evaluation from your dentist if your gums are receding in any way.
