What is geographic tongue?

Patients with geographic tongue have reddish patches with by white borders on their tongues. It's a non-contagious and harmless condition. However, if you feel discomfort or pain on your tongue, taking pain relievers and avoiding the foods that trigger the pain might be the first thing to try.
In this article, we will cover
OVERVIEW
What is geographic tongue?
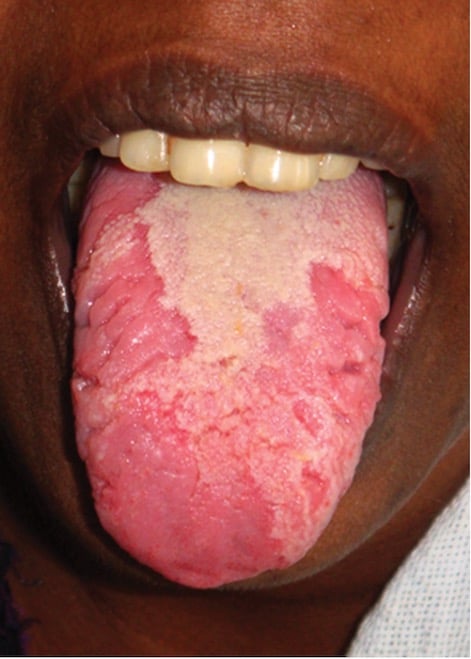
Geographic tongue is an oral condition that causes a map-like pattern on the tongue. Individuals with this condition have smooth, red patches encompassed by white border on their tongues. The red regions are feeling the loss of the little knocks (papillae) that normally show up on the outer layer of the tongue.
Geographic tongue is harmless (innocuous) and causes no long-term medical conditions. It isn't infectious. The vast majority have no side effects, yet certain individuals feel a consuming or stinging sensation on their tongue. Treatment for geographic tongue generally isn't required.
How common is geographic tongue?
Doctors aren't very sure how many have geographic tongue. Some doctors estimate that over 3% of the population might have this condition, but it may occur more frequently.
Who is affected by geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue (migratory glossitis) is somewhat common in younger adults, however, specialists do not know why. Individuals who have psoriasis (a condition that causes textured patches on the skin) and reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome) are more likely than others to have geographic tongue. The condition shows up in individuals of any age, including children and youngsters.
SYMPTOMS AND CAUSES
How do people get geographic tongue?
Doctors aren't completely sure of the causes of geographic tongue, however they do know that it is non-contagious. Because it mostly runs in families, doctors believe it might be inherited (passed down) from the parents to their children.
People with geographic tongue commonly have other conditions including:
- Psoriasis: an inflammatory skin condition.
- Hormonal surges: Women on oral contraceptives possibly due to the hormones in the pills.
- Vitamin deficiencies: zinc, iron, folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12
- Fissured tongue: a condition that creates deep grooves and or wrinkles on the tongue.
- Diabetes: People with type 1 diabetes, have a higher chance of getting geographic tongue.
- Allergies: eczema, hay fever, and other allergies.
- Emotional stress: Doctors have found a corelation between elevated stress and geographic tongue.
What are the symptoms of geographic tongue?
While most people don't notice any symptoms, the recognizable sign of a geographic tongue is the appearance of the map-like patterns on the tongue. Symptoms can come and go and might last from a few weeks to years. They include:
Red spots on the tongue: Red irregular map-like patches surrounded by white or grey borders. These patches can change in size, shape, location, and appearance over time.
Absence of papillae: The red patches are noticeably smoother as they as missing papillae. Papillae are tiny bumps that protect and coat the tongue and help in chewing food. papillae also have taste buds.
Burning sensation: Stinging, tingling, or burning sensation on the tongue, especially while eating. Discomfort is generally mild and can fluctuate in intensity.
Patches in other regions in the mouth: Occasionally, similar patches on the gums, inside the cheeks or top of the mouth.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTS
How is geographic tongue diagnosed?
Geographic tongue is diagnosed by doctors with a physical exam. Your doctor or dentist will check about your symptoms, including discomfort while drinking or eating.
How do I know if I have geographic tongue?
If you have pain and smooth, reddish spots on your tongue that looks like a map, you might have geographic tongue. While geographic tongue is not harmful, you should consult your doctor to rule out other medical conditions.
MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT
What are the treatments for geographic tongue?
As geographic tongue is a harmless condition, it doesn't require a specific treatment. If you feel discomfort or pain, you must avoid eating foods that can irritate your tongue, usually spicy food. To relieve the burning or stinging sensation, your doctor may recommend:
- Mouthwash with an antihistamine – medication to relieve allergic reaction
- Topical analgesics or pain relievers that can be applied directly to the tongue.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs
What are the side effects of the treatment for geographic tongue?
Secondary effects from NSAIDs are not severe, however they can happen. They typically just show up after somebody has taken a drug for quite a while. Symptoms of NSAIDs can include:
- Heartburn and Stomach pain
- Stomach ulcers.
- Light-headedness and Headaches
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
What are the complications associated with geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is a harmless condition with no long-term health complications.
PREVENTION
What can I do to help relieve symptoms of geographic tongue?
To relieve the burning and stinging sensation, you must avoid consuming foods that can irritate your tongue, such as spicy food or hot food. You must also avoid chewing tobacco as it can worsen the pain and stinging feeling
OUTLOOK / PROGNOSIS
What is the outlook for patients who have geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is generally harmless. Most patients have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. A small subset of people has recurring pain and/or discomfort on their tongue. They manage it with pain killers and by avoiding foods that trigger the pain.
LIVING WITH
When should I call my doctor about geographic tongue?
If you have observed symptoms of geographic tongue, you must visit your doctor or dentist to rule out other medical conditions. A swollen, red or sore tongue could also be a sign of another medical problem, so it's important to see your doctor.
