Cracked tooth syndrome: how CBCT can help in better diagnosis and treatment
Cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) is a type of tooth fracture that can be difficult to diagnose for the dentist as well as a painful and frustrating experience for the patient. When a crack occurs in your tooth, which does not completely split the tooth, or no part of the tooth is broken off, it is referred to as cracked tooth syndrome (CTS). The crack can be minor and harmless at times. If left untreated, it might also cause your teeth to crack or split. At Dental Solutions Bangalore, we deal with tooth fractures on a daily basis. The degree of the fracture and its effects might range from small, requiring no treatment, to severe, necessitating root canal therapy or even tooth loss.
Understanding Cracked tooth syndrome
Although Cracked Tooth Syndrome is more common in children and the elderly, anyone can crack a tooth.
This article will explain and help you understand the Cracked Tooth Syndrome in detail.
- Which part of a tooth is most likely to crack?
- Which teeth are most likely to fracture?
- What are the symptoms of cracked tooth syndrome?
- Cracked tooth Syndrome Diagnosis
- All About CBCT
Which part of a tooth is most likely to crack?
To understand this, let us first understand the structure of the teeth – The teeth has 2 main parts:
- Crown – The part above the gums
- The Root – The root is located beneath your gums.
And there are multiple layers in both the crown and the root. These are:
- Enamel: it has a hard white exterior.
- Dentin: which is the tooth's middle layer.
- Pulp: Blood vessels and nerves are found in the pulp, which is soft inner tissue.
Cracked tooth Syndrome or a fractured tooth can affect some or all of these parts. Remember, the treatment for a cracked tooth is determined by the location of the fracture and the severity of the fracture.
Although some fractures create no symptoms, a broken tooth may exhibit pain or feel sensitive most of the time. It is important to understand the symptoms of Cracked Tooth Syndrome (CTS). Getting treatment for a CTS as soon as possible enhances the chances of it being repaired- and more importantly, saved.
Which teeth are most likely to fracture?
Noticing symptoms is extremely important to get them diagnosed at the dental clinic. At times there might be no symptoms, unfortunately, in these cases, by the time an incomplete tooth fracture becomes symptomatic, the tooth may be too far gone to be saved. Routine clinical examinations are one way to reveal obvious fracture lines.
What are the symptoms of cracked tooth syndrome?
1. Sharp pain when chewing on a particular tooth, which may worsen if the biting force used is increased.
2. Pain when chewing or biting
3. Rebound pain – a sharp pain that occurs when the biting force from the teeth is released
4. Pain when grinding the teeth back and forth, as well as side to side
5. Sensitivity to hot or cold food.
6. Pain is experienced when consuming sugary food or beverages.
7. Swelling around the tooth or inflamed gums
Cracked teeth don't always cause symptoms, if you notice any of the above you need to seek dental consultation immediately. But how will the dentist diagnose Cracked Tooth Syndrome?
Cracked tooth Syndrome Diagnosis
CTS diagnosis has proven difficult for dentists for years – Because the discomfort or pain seems similar to that of other ailments such as sinusitis, temporomandibular joint disorders, headaches, ear pain, or orofacial pain. However, modern dentistry, along with technology has carved paths that are making diagnosis simpler.
Some of the methods of Diagnosis of CTS are:
- Clinical Examination through Visual Inspection –
Although a visual examination of the tooth is beneficial, cracks are often not evident without the use of magnifying loupes. It can be identified on rare occasions. However, it is not always obvious.
- Tactile Examination –
Using the tip of a sharp explorer, scratch the tooth's surface. If there's a crack, it's possible that the tip will be caught in the crack.
- Excavation for Exploratory Purposes
In order to achieve a visual diagnosis, exploratory excavation is sometimes required. Because it is not assured that a fracture will be found behind any removed restoration, the dentist will require the patient's agreement to go ahead with the diagnosis. Existing restorations may disclose fracture lines if they are removed.
- Periodontal Probing
When the fracture line extends below the gingiva, generating a localized periodontal defect, periodontal probing can help distinguish between a cracked and a split tooth. Careful probing of suspected fissures is required to reveal the presence of an isolated periodontal pocket. However, this might be time-consuming and very rarely inaccurate.
- Dye Test
Fracture lines can be highlighted with gentian violet or methylene blue stains. The disadvantage of this method is that it takes at least 2–5 days to work and may necessitate the use of a temporary repair (a provisional restoration).
- Other Tests are – Clinical or Wedge tests, Transillumination, Bite Tests and conventional radiographs.
Clinical examination, sometimes known as a wedge test, seeks to duplicate the pain by applying stress to each suspected tooth, although this risks increasing the crack's severity. In conventional radiographs, Because of the projection geometry of conventional radiographs, any crack lines that do not run in the same direction as the X-ray beam are hidden and not seen in a periapical radiograph. If the troublesome tooth is not found quickly, it may break later, rendering the tooth unfit for saving. The ability to detect a fracture and see how far it has spread with high-resolution CBCT equipment is quite appealing.
What is Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)?
Dental cone beam computed tomography (CT) is a type of x-ray system that is utilized when standard dental or face x-rays aren't enough. In a single scan, your doctor may be able to obtain three-dimensional (3-D) images of your teeth, soft tissues, nerve pathways, and bone. Dental professionals use CBCT devices that circle around the patient and capture data with a cone-shaped X-ray beam.

Although both CBCT and CT provide high-quality images. Cone beam CT is not the same as conventional CT. When compared to standard CT, cone beam CT provides a reduced radiation dose.
What is the benefit of using CBCT in treating cracked tooth syndrome?
Most of the above diagnosis methods may fail to detect a CTS, but with CBCT, CTS can be identified from the beginning till the end. Besides this major benefit, there are other benefits as well:
- The reduced scatter radiation from the focussed x-ray beam improves image quality.
- A single scan generates a wide range of views and angles, which can be adjusted to provide a more comprehensive assessment.
- Cone beam CT scans are more detailed than traditional dental x-rays, allowing for more exact treatment planning.
- CBCT scanning is noninvasive, painless, and accurate.
- The capacity of CBCT to examine both bone and soft tissue at the same time is a significant advantage.
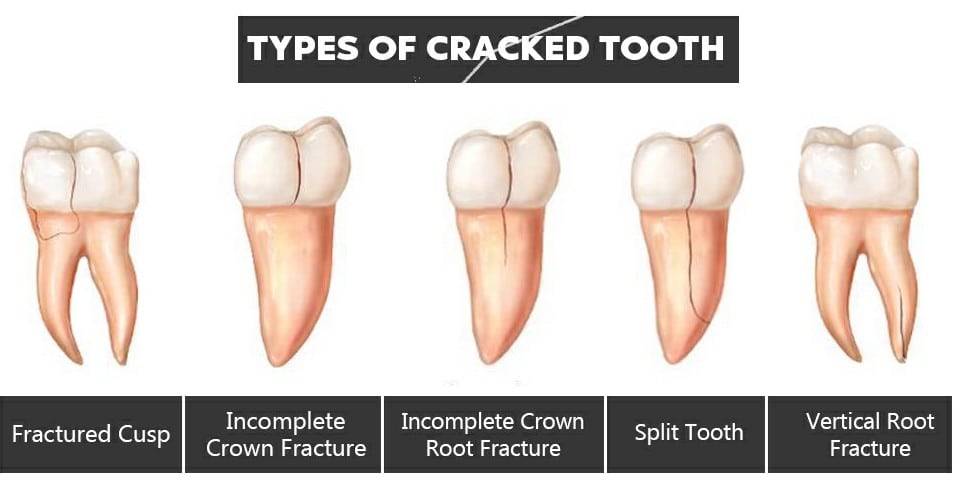
Once diagnosis via CBCT is done, the dental professionals will plan your treatment as per the classification of the crack.
- A simple crown fracture
- A crown fracture, exposing the dentin, but no pulp exposure
- Extensive crown fracture, exposing the pulp
- Root fracture with or without crown structural loss.
- Traumatic tooth loss – Where the tooth cannot be saved.
Depending on the classification various treatment plans will be curated – Root Canal therapy will be advised as required.
Cracked Tooth Syndrome in its early stages is not easy to identify, hence, we urge you not to miss out on any dental appointments. Routine check-ups can help identify them early.
For all treatment options on CTS, reach out to one of the best dental professionals in Bangalore – Dental Solutions!
